
This development gives Honda a clear advantage as the industry moves closer to commercial deployment of solid state batteries.
Share Post

This development gives Honda a clear advantage as the industry moves closer to commercial deployment of solid state batteries.
Honda is striving to realise full carbon neutrality for all its products and corporate activities by 2050. The Japanese carmaker has now taken a significant step in this direction. Honda has moved beyond laboratory research and future-facing announcements by commencing operations at its solid-state battery (SSB) demonstration production line in Japan.
This development marks one of the most tangible advances in solid-state battery technology by a global automaker and positions Honda as a frontrunner in translating next-generation battery concepts into manufacturable reality.
The demonstration facility is located in Sakura City, Tochigi Prefecture, and is designed to validate the manufacturing processes required for large-scale solid-state battery production. Spanning approximately 27,400 square metres, the plant represents an investment of around ¥43 billion (₹24.5 billion). Honda began production on this pilot line in January 2025, underscoring its intent to move decisively from research and development into industrial application.
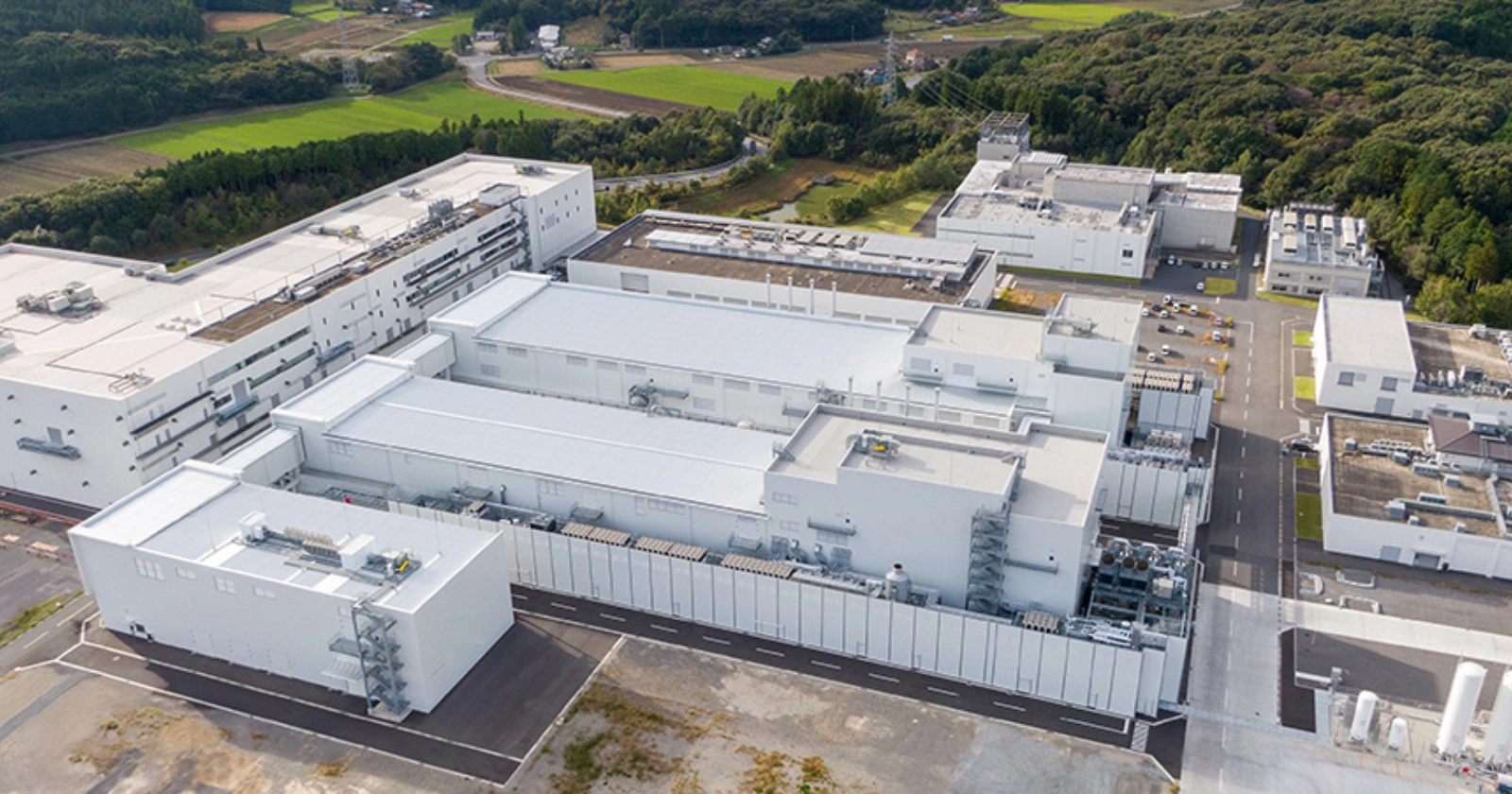
Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries replace liquid electrolytes with solid materials. While this promises significant performance and safety benefits, it also introduces new production challenges. Honda’s demonstration line is focused on verifying processes such as material mixing, electrode coating, roll pressing, and module assembly—critical steps for achieving consistent quality and scalability.
A key technological highlight of Honda’s solid-state battery effort is its use of a roll-pressing technique during cell assembly. This process compresses solid electrolyte layers, improving contact between electrodes and the electrolyte while reducing internal resistance. Enhanced layer bonding is crucial for improving energy efficiency and long-term durability—two factors that have historically limited the viability of solid-state batteries.
By refining this manufacturing approach, Honda aims to address one of the most persistent barriers to solid-state adoption: achieving reliable performance at scale. The company also believes that solid-state batteries will allow for simplified cooling systems, given their higher tolerance to heat compared to conventional liquid-electrolyte battery packs.
One of the most significant technical challenges in solid-state battery development is dendrite formation. These microscopic lithium crystal structures can grow during repeated charging cycles and eventually cause internal short circuits, compromising battery life and safety.
Honda is addressing this issue by incorporating a thin polymer layer at critical interfaces within the battery cell. This barrier is designed to suppress dendrite growth, thereby extending battery lifespan and improving reliability. Managing dendrites effectively is widely regarded as a prerequisite for making solid-state batteries commercially viable, particularly for automotive applications.
Honda’s solid-state battery ambitions extend well beyond passenger electric vehicles. The company sees potential applications across multiple mobility segments, including motorcycles, commercial vehicles, and even aviation-related use cases. This broader outlook aligns with Honda’s long-standing identity as a diversified powertrain and mobility solutions provider.
Honda has indicated that it aims to deploy solid-state batteries in production vehicles in the latter half of the 2020s, with a market introduction realistically expected around 2028. By leveraging economies of scale across various product categories, Honda aims to reduce per-unit battery costs over time. Cost reduction remains a critical factor, as solid-state batteries are currently more expensive to produce than conventional lithium-ion alternatives.
Also READ: BMW Previews Electric M3 Ahead of 2027 Launch
Solid-state battery development forms a central pillar of Honda’s long-term sustainability strategy. The company has committed to transitioning its global vehicle lineup to electric and hydrogen-powered models by 2040, with the ultimate objective of achieving carbon neutrality across its operations by 2050.
From an EV adoption standpoint, solid-state batteries offer solutions to several persistent consumer concerns, including charging time, range limitations, and thermal management. Improved energy density and faster charging potential could make electric vehicles more practical for a wider audience, supporting Honda’s broader electrification roadmap.
Maruti Suzuki Inaugurates 200th Nexa Studio Outlet, Bets Big On Rural Market
Sameer Fayaz Contractor 27 Feb, 2026, 3:04 PM IST
Chinese Firm Reveals Detachable Range-Extending Generator for EVs
Acko Drive Team 27 Feb, 2026, 12:12 PM IST
Non-PLI Electric Two-Wheeler OEMs See Growth Plunge from 407% to –33%: Report
Acko Drive Team 27 Feb, 2026, 11:48 AM IST
51 Teams Compete as mBAJA SAEINDIA 2026 Opens in Narsapur
Acko Drive Team 27 Feb, 2026, 10:05 AM IST
Maharashtra Tops India PV Sales in Q3 FY2026 With 12.4% Share, Western Zone Leads All Regions: SIAM
Acko Drive Team 27 Feb, 2026, 9:39 AM IST
Looking for a new car?
We promise the best car deals and earliest delivery!
